The stock market Crash 2025 in india is a mirror reflecting the economic sentiments of a nation. In January 2025, India witnessed a significant market crash that shook investors, companies, and policymakers alike. This article delves into the factors leading to the crash, its immediate consequences, and what investors can learn from this financial turmoil.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is a Stock Market Crash?

A stock market crash is a rapid and significant decline in the prices of stocks across major exchanges. It is often triggered by economic instability, geopolitical events, or market speculation. Stock Market Crash 2025 in India was no exception, causing panic and eroding investor confidence.
Causes of the Stock Market Crash in India 2025
1. Global Economic Slowdown
The slowdown in global markets contributed heavily to India’s stock market crash. Factors like reduced demand for exports, rising inflation in developed countries, and monetary tightening by central banks created an environment of uncertainty.
2. Weak Domestic Economic Indicators
The stock market Crash 2025 in india.India’s economic performance showed signs of stress in late 2024, with slowing GDP growth and rising fiscal deficits. Persistent inflation in key sectors such as energy and food further exacerbated the situation.
3. Geopolitical Tensions
Rising tensions in South Asia and strained relations with neighboring countries created additional pressure on market sentiments.Stock Market Crash 2025 in India Investors pulled back due to fears of potential instability.
4. Tech Sector Bubble Burst
A tech bubble that had been inflating due to overvaluation of startups and AI-based companies finally burst in 2025. Over-leveraged companies struggled to justify their valuations, leading to a ripple effect across the market.
5. Panic Selling by Retail Investors
The cascading effect of Stock Market Crash 2025 in India panic selling among retail investors aggravated the crash. Lack of financial literacy and herd behavior resulted in widespread losses.
Immediate Consequences of the Crash
- Market Indices Plummet
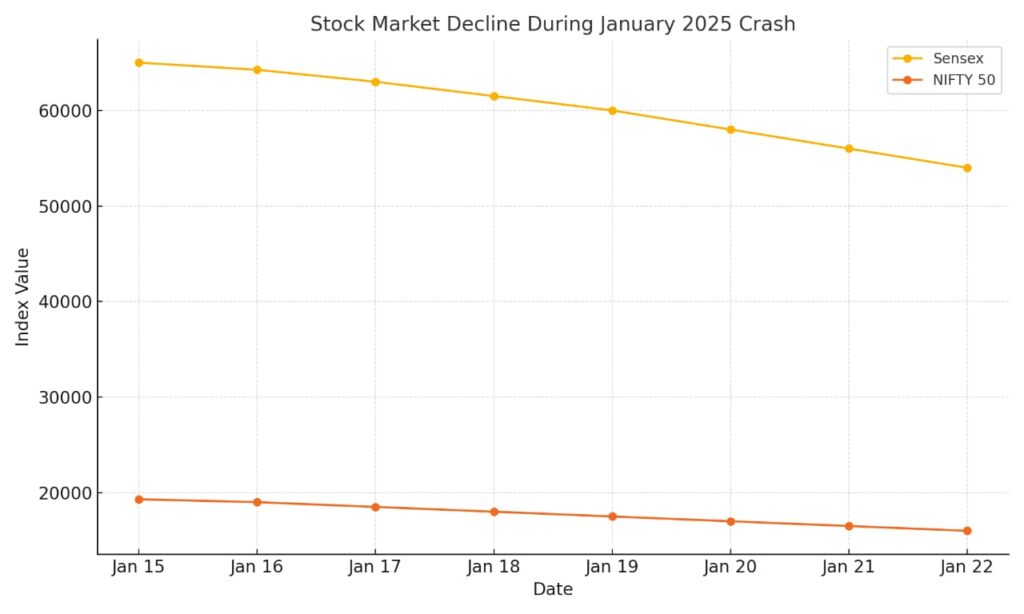
Key indices like the NIFTY 50 and BSE Sensex dropped by over 20% within a week, wiping out billions in market capitalization.
- Job Losses in Financial and Tech Sectors
Companies across various sectors, especially IT and financial services, announced layoffs, adding to economic distress.
- Decline in Investor Confidence
Institutional and retail investors lost faith in the markets, leading to liquidity issues. Mutual funds and equity investments saw record redemptions.
- Impact on Indian Rupee
The Indian Rupee depreciated significantly against the US Dollar, further exacerbating inflation and increasing the cost of imports.
Sectoral Analysis of the Crash
- IT and Tech Sector
Once a darling of the stock market, the IT sector suffered the most due to the bursting of the tech bubble. Declining demand for AI products and overspending on R&D contributed to the crisis.
- Banking and Finance
The banking sector faced mounting Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) as businesses defaulted on loans, leading to declining profits and a crisis of confidence.
- Real Estate and Infrastructure
Real estate projects stalled as funding dried up. Infrastructure companies faced delays, leading to a slowdown in construction activity.
- Energy Sector
Rising crude oil prices and reduced government subsidies put additional stress on energy companies.
Government and Regulatory Response
- Measures Taken by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
The RBI introduced emergency liquidity measures to stabilize the market. Interest rates were adjusted to control inflation and provide relief to borrowers.
- Fiscal Policies by the Government
The government announced stimulus packages, including tax cuts and financial support for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), to revive the economy.
- Reforms in Corporate Governance
Regulatory authorities introduced stricter norms to curb speculative activities and improve corporate governance standards.
Lessons for Investors
- Diversification is Key
Investors learned the importance of not putting all their eggs in one basket. Diversified portfolios weathered the storm better.
- Importance of Financial Literacy
The crash highlighted the need for greater financial literacy among retail investors to avoid panic selling and irrational decisions.
- Staying Updated with Economic Indicators
Being aware of global and domestic economic trends can help investors make informed decisions.
Comparing the 2025 Crash to Past Crashes
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis
While the 2008 crisis was triggered by subprime mortgages in the US, the 2025 crash was a mix of global and domestic factors, including tech overvaluation.
- COVID-19 Crash in 2020
The pandemic-induced crash was abrupt but short-lived, whereas the 2025 crash has shown prolonged effects.
Road to Recovery: What Lies Ahead?
- Stabilization of Market Indices
Experts predict a gradual recovery in market indices as investor confidence returns.
- Growth in Emerging Sectors
Sectors like renewable energy, healthcare, and agritech are expected to drive future growth.
- Strengthening Economic Policies
The government and RBI are likely to focus on policies promoting sustainable growth and financial stability.
Conclusion
The stock market crash of 2025 in India serves as a wake-up call for all stakeholders. It highlights the interconnectedness of global and domestic economies and the need for cautious optimism in the face of volatility. By learning from the mistakes of the past and implementing robust financial practices, India can emerge stronger from this crisis.
Investors must remember that every crash is also an opportunity to rebuild and innovate. The key lies in staying informed, diversified, and patient during such turbulent times
The Indian stock market crash of 2025 was triggered by global economic slowdown, domestic economic challenges, tech sector overvaluation, and panic selling among investors.
Indian investors faced significant losses due to declining stock prices, reduced mutual fund returns, and increased market volatility, leading to panic selling and reduced confidence.
The IT and tech sectors, banking and finance, real estate, and energy sectors were hit hardest by the crash due to overvaluation, rising costs, and economic instability.
Recovery efforts include government stimulus packages, RBI’s liquidity measures, corporate governance reforms, and the growth of emerging sectors like renewable energy and healthcare.
